Introduction - Compliance and Documentation
At AWS, there is an exhaustive list of compliance sets for your organization. I will be exploring how to create a HIPAA-compliant AWS instance complete with functional IAM roles, group policies, S3 storage, EC2 instances, and CloudWatch (among other services) for managing the future applications and resources that will one day support protected health information (PHI) security standards.
According to AWS official documentation, it is important to know that just because your company launched an AWS Instance with a Quick Start compliance stack, it does not guarantee that you will be fully compliant from the get-go with your company’s specific regulations. You need to make sure in your own time with your own auditors that the way that user data is being handled is compliant with your specific rules and regulations.
Using Quick Starts
For this tutorial, we will be following along with this guide from AWS itself and we will be using the Quick Start feature that AWS provides. It uses stacks to build pre-defined infrastructure connections. Here is the example diagram shown by AWS: 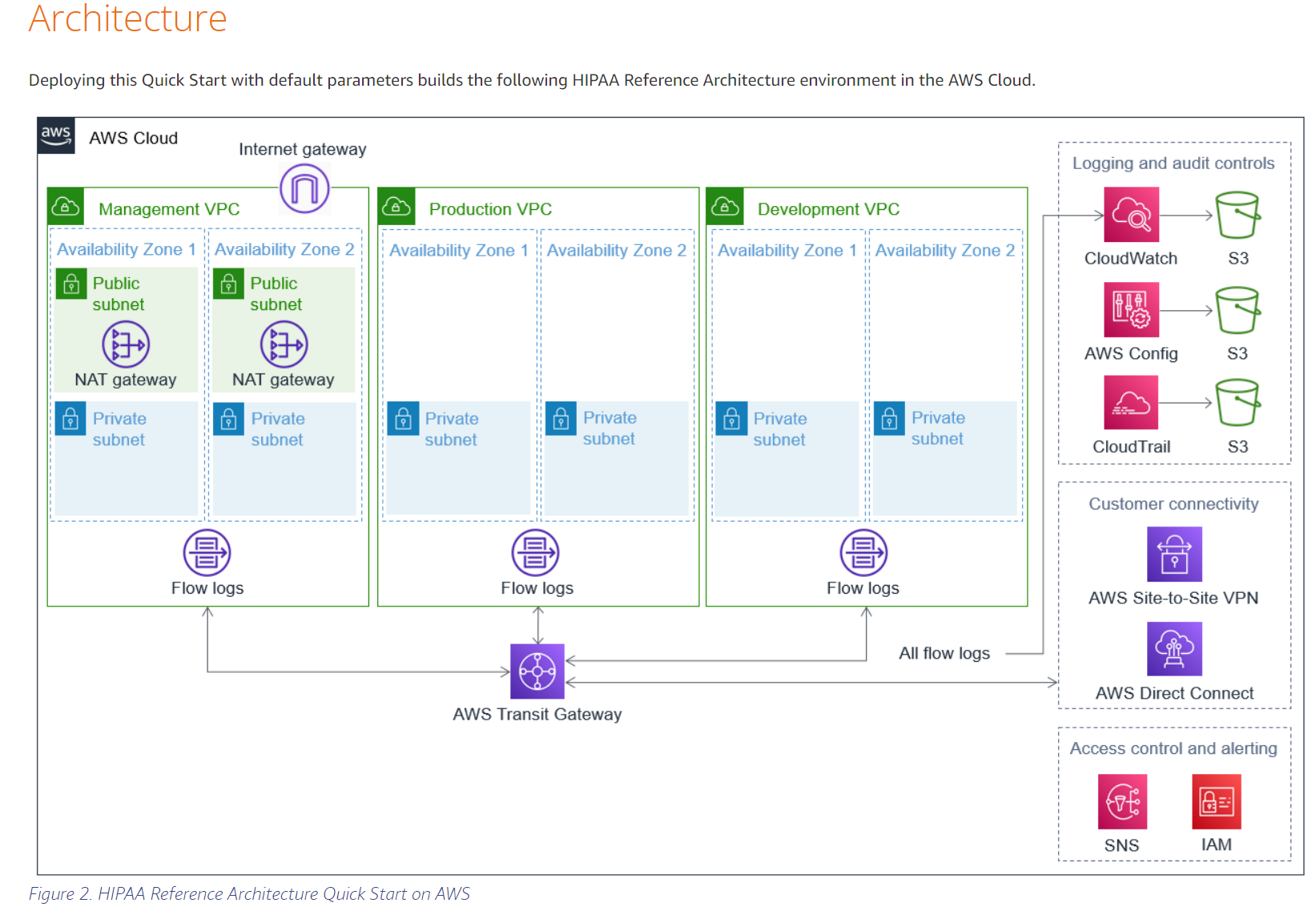
To view a list of AWS Quick Start templates, go to https://aws.amazon.com/quickstart/. You should be greeted with a friendly landing screen that allows you to search templates that may fall into your organization’s needs. 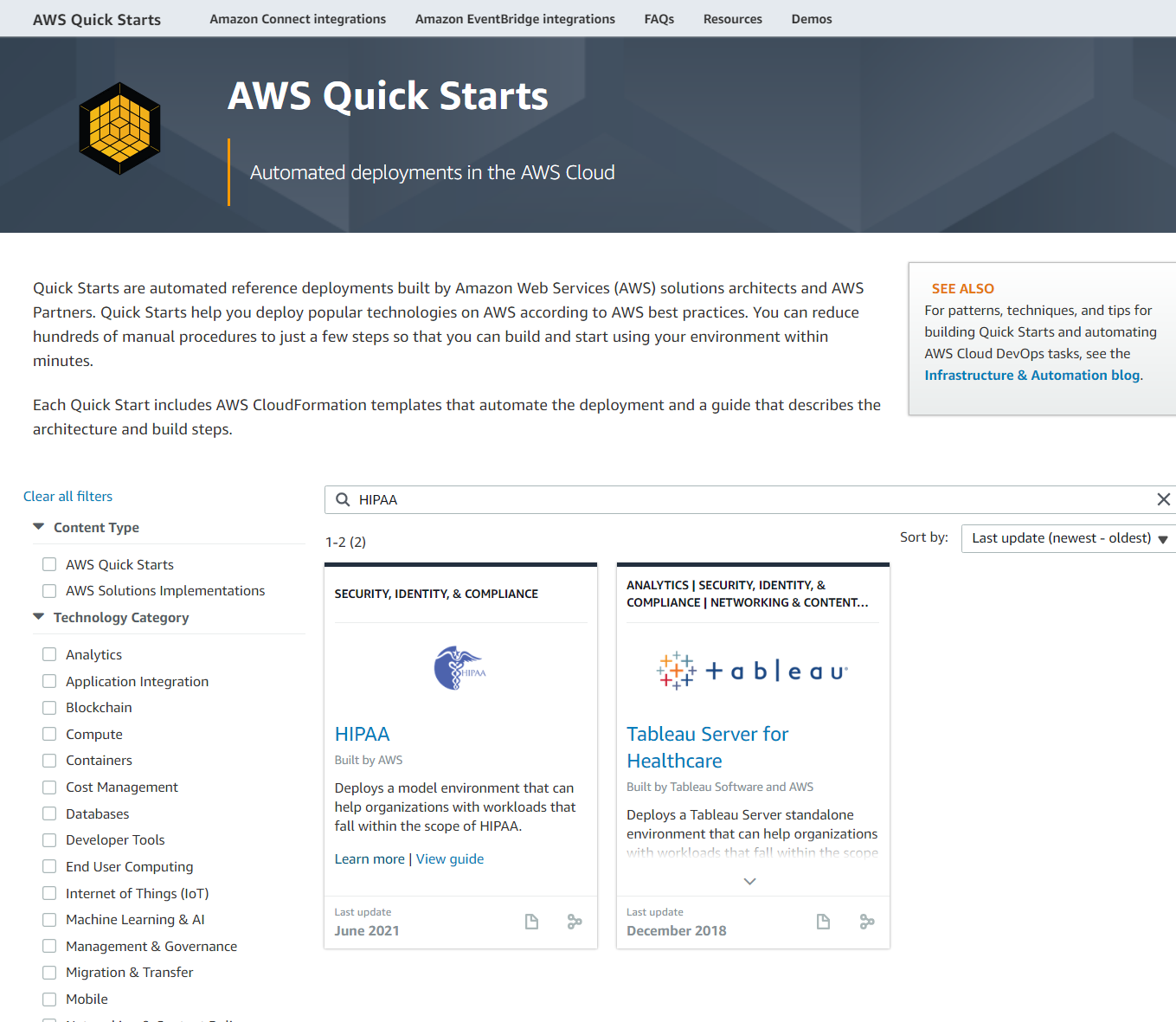
For this tutorial we are attempting to follow HIPAA standards, or at least begin with a baseline to help ease us into the process of making appropriate rules. Next, I click on the how to deploy prompt and click on step 2, assuming you are signed into the appropriate AWS account that you want to create this infrastructure on. Click launch the quick start and it will bring you to a Quick Create Stack page in your AWS Management Console. From here, I recommend making your own custom Stack Name for this stack, probably something having to do with HIPAA, especially if you plan to test out multiple configurations of this Stack and make it fit your organization’s specific needs. This will cut down time on confusion of which stack you are fiddling with, especially if you wish to test out specific permissions or AWS Config settings on a copy of this existing stack.
It is worth noting that Stacks are a part of CloudFormation, which is essentially AWS’s template service for (For lack of a better term) automating deployments of instances that need to be built quickly. Of course you can create your own Stacks just the same way that this HIPAA was built, but that’s a little more involved of a process. We’re here to save time for now!
Understanding Documentation
Let’s take a step back and examine the deployment plan in the quick start tab before we actually launch this stack. 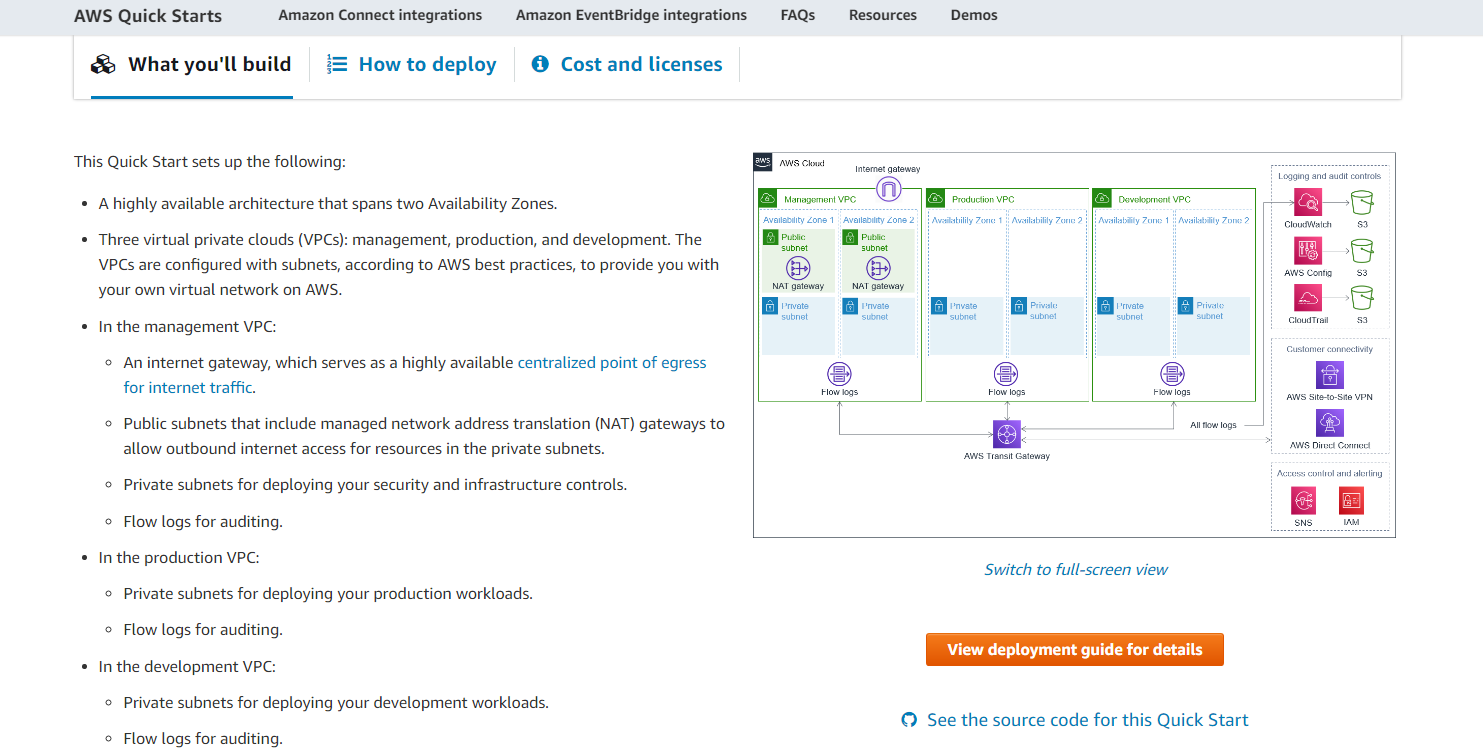
This opens up yet another tab where we can see a full breakdown of pertinent information provided by the team that created the Stack you are about to implement. 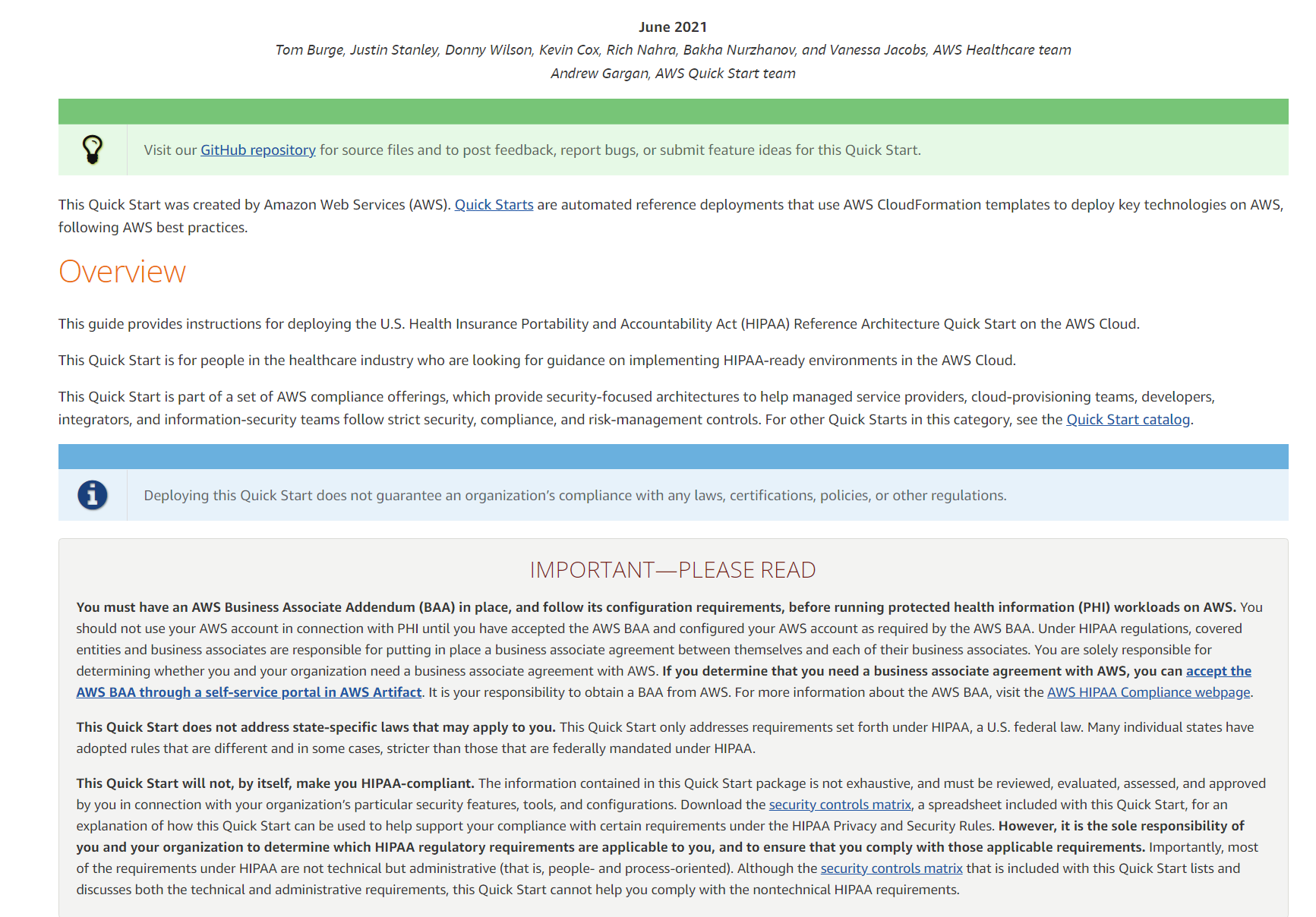
Right away by examining this document, we can see important compliance rules that you will have to consider. In order to be compliant with HIPAA regulations, even before entering any PHI into your shiny new instance, it is stated that you must have an AWS Business Assocaite Addendum (BAA). It even provides you with a link on where to accept the AWS BAA agreement. Let’s go there since they were kind enough to provide the link.
The link provided by the document will bring you to AWS Artifact. Click on the upper right hand corner link view agreements and you will be greeted by this lovely pane. 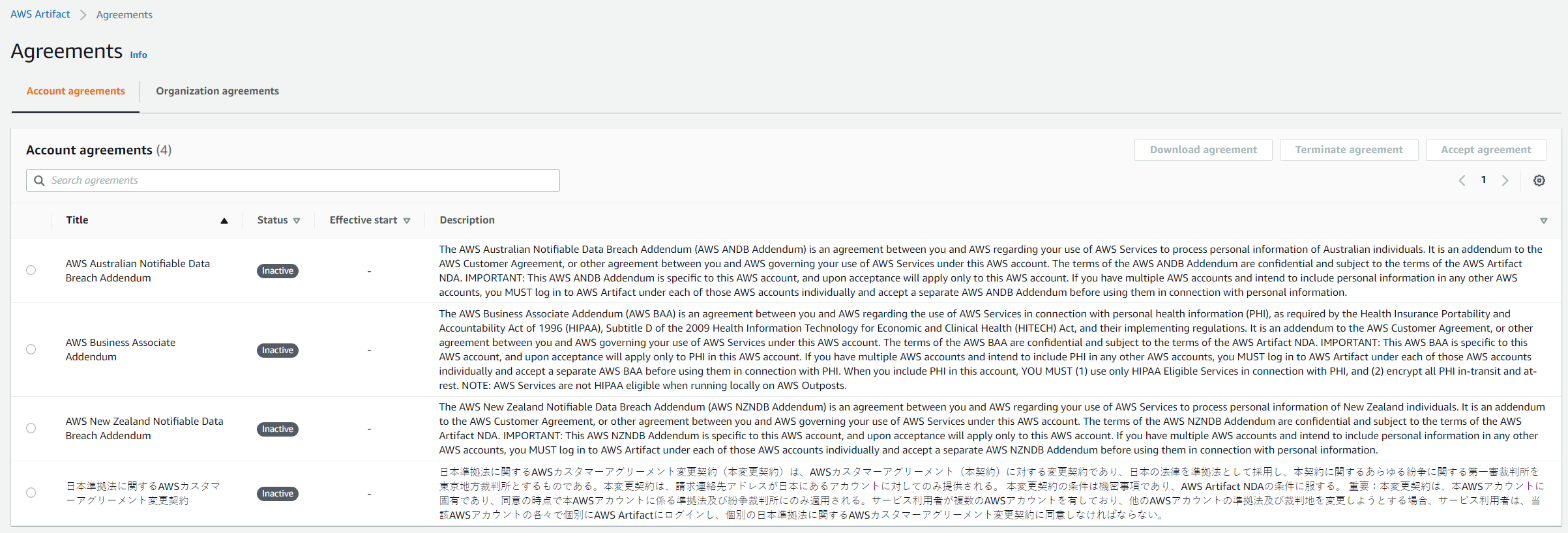
Carefully read through the AWS BAA agreement documentation if your organization requires you host PHI on the AWS Infrastrcuture. Once done, click the bubble on the left of the AWS BAA, click accept agreement and you can return to your Cloud Formation page to finish this process.
Throughout the Parameters section, you can change various aspects of services such as CloudTTrail log-in retention days, S3 LIfecycle settings, and plenty of other VPC configuration settings. These are all personal preference settings for the most part, and some may very well depend on your company’s compliance and regulation standards. Whatever the case may be, once you have configured the stack to your liking, it is time to agree to the Capability agreeements now and select Create Stack. You will be brought to a page that looks like this: 
You will notice that this is a CloudFormation page. Any time you use stacks in this way, you will ultimately be dealing with AWS CloudFormation.
Conclusion
While AWS Quick Starts can be useful in creating baseline compliance readiness, they do still need to be reviewed by your company’s internal regulation technicians and auditors. AWS thankfully provides many useful regulation documents as discussed above, however it is ultimately your company’s responsibility to create, maintain, and update your infrastructure within AWS to fit your compliancy needs.