Introduction - Checking Available Interfaces
This post is focused around configuring a BackTrack (Linux-based) machine to become a Linux-based firewall. Virtual machines from NetLab were used for illustration purposes.
First, enter your BackTrack machine and open a new Konsole tab. Type ifconfig -a to view all available network interfaces. 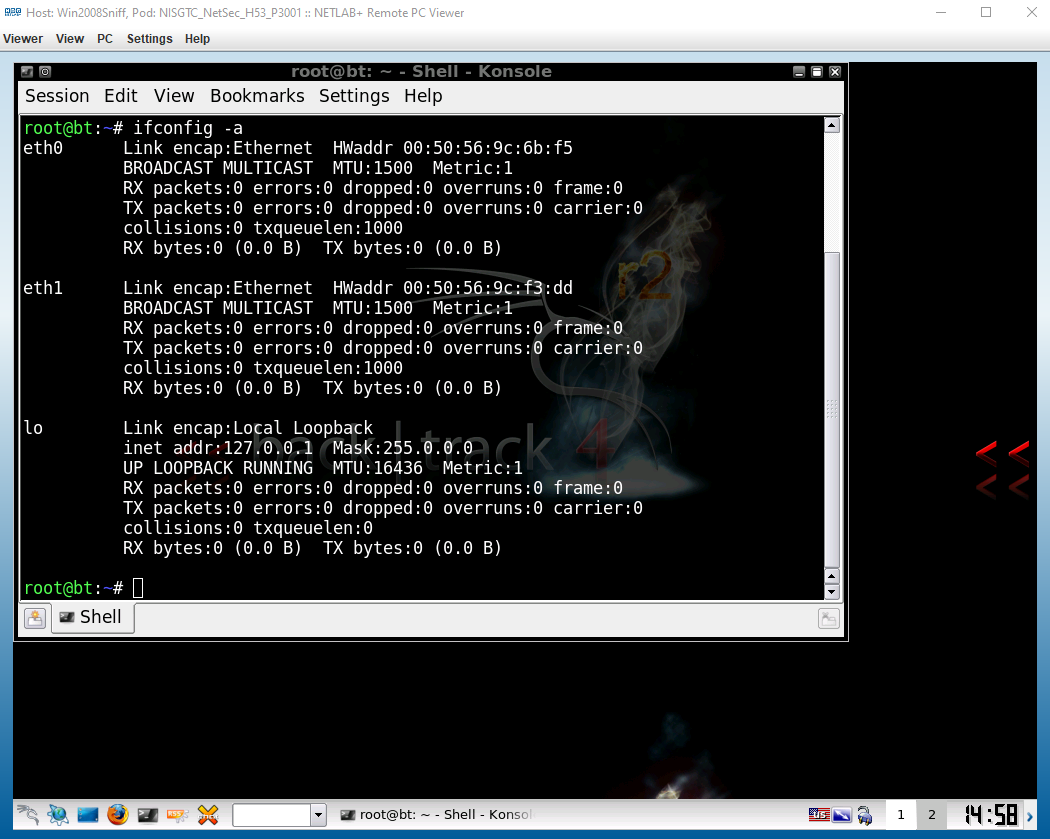
Setting Internal Addresses
We will use the eth0 to set the internal IP address of this Sniffer machine, using the format ifconfig nameofinterface, IP address, netmask net.mask.here.x, up as shown. 
We will then also configure the IP address of the Sniffer Server in a similar manner, but this time using eth1’s information. 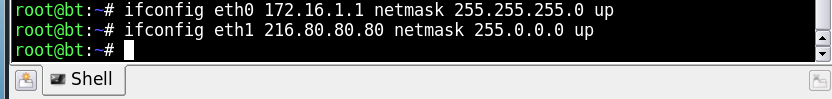
For the next step, we will be using a machine that is running Backtrack 5r3. We will use this machine to set a static address on the BackTrack 5 R3 machine in a similar manner to how we set the internal and server IP addresses. The difference is that this time, we will need to also set the gateway of the BackTrack machine by using the route command as shown. Netstat -r will show us the gateway. 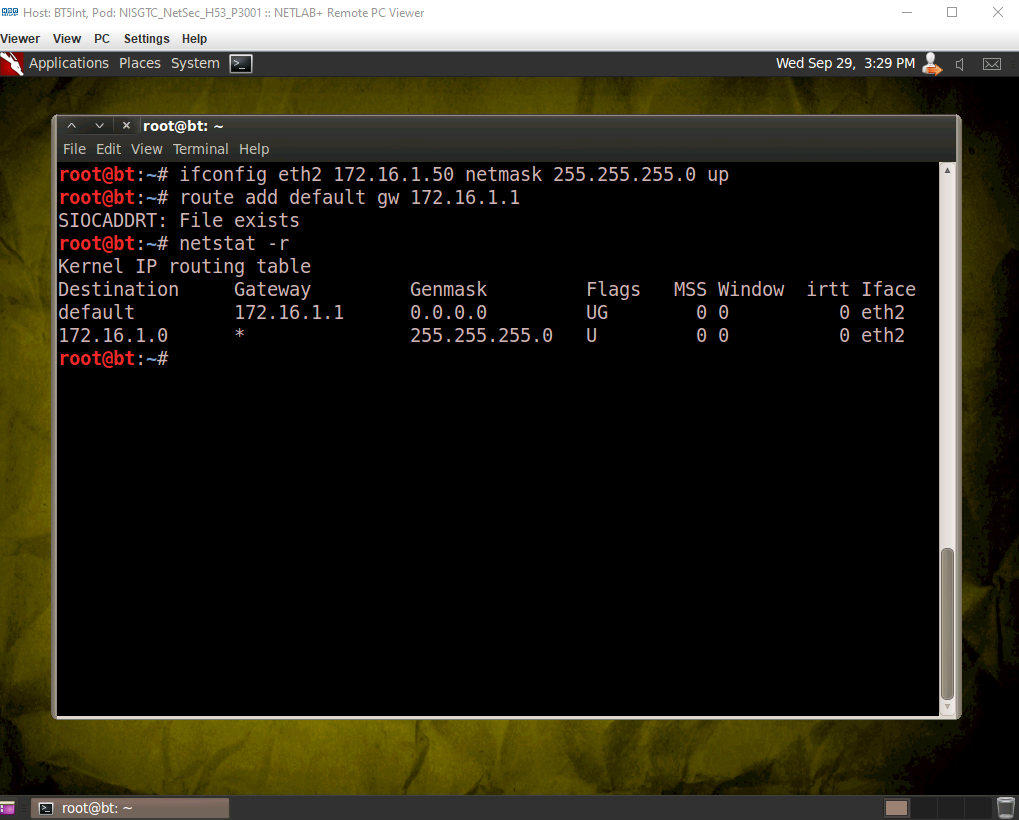
Testing the Gateway
Try to ping the gateway from the BackTrack 5 R3 machine (in our case, the gateway’s address is 172.16.1.1, and we will use the -c option to ping it 4 times as shown.) 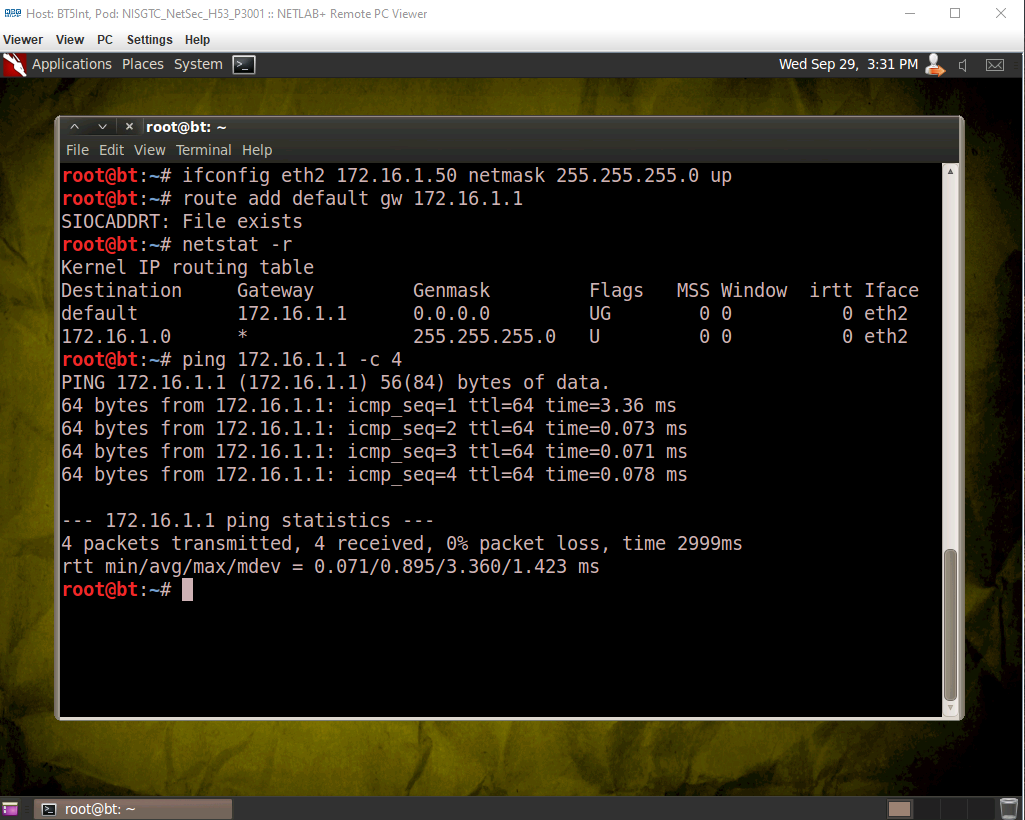
If that worked fine, then try to have a friend who has an external machine (read: any computer with a command prompt that is outside of your network) ping the external IP address of the sniffer to check if it was configured correctly. They should receive responses like this: 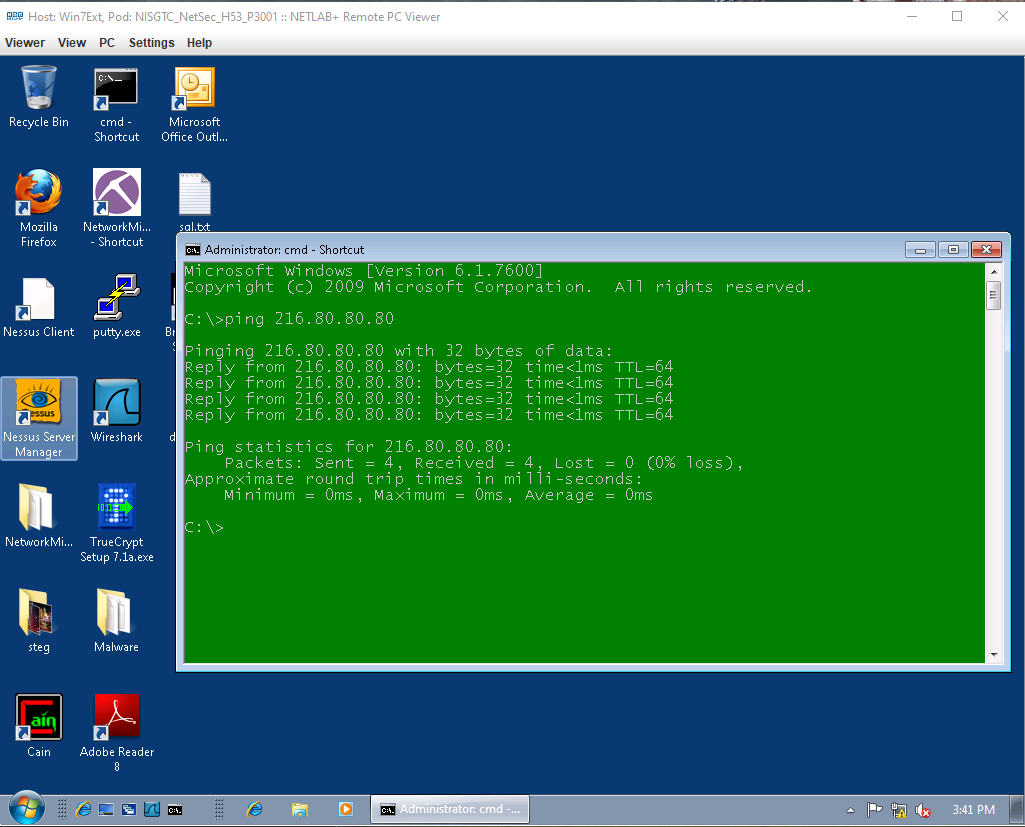
If your friend got responses to their ping request, then you successfully configured both the Sniffer Server and the gateway! Congratulations.